Presentation of the NanoBAP Project
Fresh and processed foods are perishable foods that need to be properly packaged to preserve their sensory and safety qualities, by protecting them from external factors, and extending their shelf-life by preventing microorganisms’ invasion and spoilage. In addition, in order to fulfil consumers’ expectations for healthy food, the new requirement engineering of packaging materials should follow new natural compounds by substituting synthetic/chemical antimicrobial (AM) and antioxidant (AO) agents. Trend toward green consumerism with increased consumer awareness for less use of chemical preservatives, has increased the demand of naturally derived AO and AM. Thus, research and innovation in food packaging have become a significant challenge, and led to the development of Active food Packaging (AP).
In NanoBAP project, we propose an environmentally friendly process to develop new active food packagings for the combined release of multiple antimicrobial natural compounds. More precisely, active antimicrobial coatings based on biosourced materials will be designed by electrospinning applied directly onto a biaxially stretched polylactide (PLA) film. These nanofibrous coatings will be loaded with antimicrobial natural substances such as essential oil (EO) extracts, antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) and phenolic compounds. This new type of AP will exhibit enhanced release properties, antimicrobial efficacy against a wide range of microorganisms and antioxidant activities while maintaining excellent mechanical, barrier and biodegradability properties. All components used for the elaboration of this multifunctional active packaging are biodegradable, safe and food grade.
Two strategies will be fully investigated, from the design and characterisation of physico-chemical properties of the coated films and the combined release/transfer mechanisms of active compounds up to the evaluation of in vitro and model/simplified food antimicrobial activity. The final innovative proposed packaging solution would be of key importance for the packing of sliced or textured fresh foods.
In conclusion, the outcome of this project will generate fully bio-based and biodegradable active films with the potential to substantially mitigate plastic pollution and to reduce food waste. This will make a both scientific and economical step forward to “zero waste” concept.
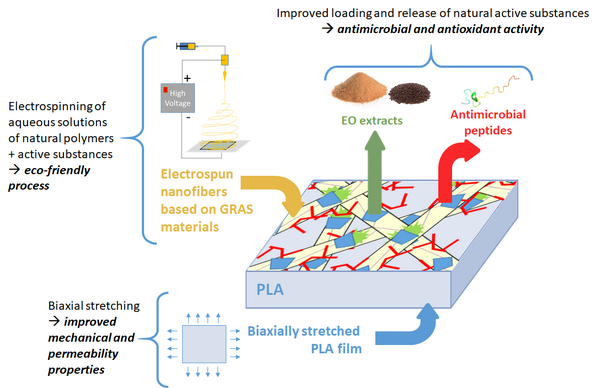
The strategy of NanoBAP project is based on three complementary approaches to develop innovative smart food packagings:
- the biaxial stretching of food contact PLA film in order to improve the mechanical and barrier properties,
- the use of an eco-friendly process through the electrospinning of aqueous solutions of natural polymers and active substances
- and the improved loading and release of natural active compounds in order to target a prolonged antimicrobial and antioxidant activity.





